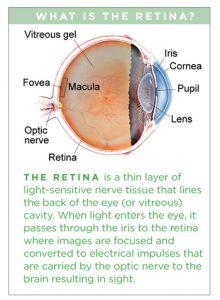
The vitreous humor is a transparent, gel-like material that fills the space within the eye between the lens and the retina. The vitreous is encapsulated in a thin shell called the vitreous cortex, and the cortex in young, healthy eyes is usually sealed to the retina.
As the eye ages, or in certain pathologic conditions, the vitreous cortex can pull away from the retina, leading to a condition known as posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). This detachment usually occurs as part of the normal aging process.
There are instances where a PVD is incomplete, leaving the vitreous partially attached to the retina, and causing tractional (pulling) forces that can cause anatomical damage. The resulting condition is called vitreomacular traction (VMT) syndrome.
VMT syndrome can lead to different maculopathies or disorders in the macular area (at the center of the retina), such as full- or partial-thickness macular holes, epiretinal membranes, and cystoid macular edema. These disorders are often associated with reduced sharpness of vision (visual acuity) or other visual complications.
SYMPTOMS IN DETAIL
The most common symptoms experienced by patients with VMT syndrome are:
- Decreased sharpness of vision
- Photopsia, when a person sees flashes of light in the eye
- Micropsia, when objects appear smaller than their actual size
- Metamorphopsia, when vision is distorted to make a grid of straight lines appear wavy or blank
Some of these symptoms can be mild and develop slowly; however, chronic tractional effects can lead to continued visual loss if left untreated. In some cases, a distortion of a visual picture could be experienced without necessarily having a reduction in sharpness of vision.
Causes
Age-related degeneration of the gel-like vitreous humor leads to the formation of pockets of fluid within the vitreous, causing contraction and loss of volume. The separation of the vitreous gel from the retina occurs as a result of the gel becoming liquid (liquefaction) and the continuous anterior-posterior (front-back) and tractional forces stretching on the macula over time.
Weakening of the attachments of the vitreous cortex and the internal limiting membrane (ILM) of the retina could also lead to partial detachment of the posterior hyaloid membrane, leading to PVD and potentially VMT.
RISK FACTORS
VMT syndrome is most common in older adults and women due to age-related vitreous changes and vitreous liquefaction associated with declining post-menopausal estrogen levels, respectively.
- Other risk factors include:
- High myopia (extreme nearsightedness)
- Exudative (wet) age-related macular degeneration
- Diabetic macular edema
- Retinal vein occlusion
- Diabetic retinopathy
Treatment and prognosis
There are currently 3 main options for treating VMT syndrome.
- 1. Watchful waiting and regular monitoring with OCT is often used for patients whose symptoms do not warrant active intervention. Some cases of VMT may spontaneously resolve.
- 2. For patients whose symptoms are severe enough to require intervention, pars plana vitrectomy surgery is one treatment option. The procedure involves the manual release of vitreous attachment and alleviation of traction, but it is invasive and inconvenient to most patients. Therefore vitrectomy is reserved for patients who are at risk for severe visual disturbances and/or central blindness. Some studies have shown that shorter duration of symptoms results in better prognosis when the surgical treatment is employed.
Most patients with VMT maintain good visual acuity in the affected eye, even if treatment is required.